Secure Communication

General Description
The Secure Communication component installs, issues, and revokes digital certificates, which are strictly necessary to securely exchange information between ZDMP assets and external resources. From the Security Command Centre UI, the administrator can revoke, renew, and install certificates.
This component includes a Certification Authority (CA) and a Registration Authority (RA). These are the core of this component and is responsible for issuing/revoking certificates and matching identities with certificates, respectively.
| Resource | Location |
|---|---|
| Source Code | Link |
| Open API Spec | Link |
| Video | Link |
| Online documentation | Link |
Screenshots
The following images are illustrative screen shots of the component.
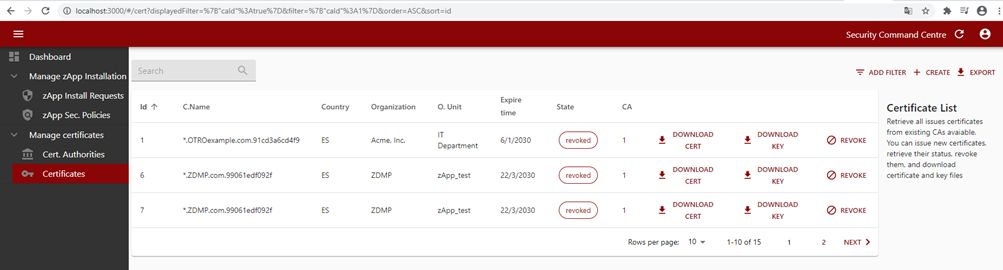
Figure 32: Security command centre certificates list
Component Author
| Company Name | ZDMP Acronym | Website | Logo |
|---|---|---|---|
| Instituto Tecnológico de Informática | ITI | www.iti.es |  |
Commercial Information
| Resource | Location |
|---|---|
| IPR Link | Link |
| Marketplace Link | Link |
Architecture Diagram
The following diagram shows the position of this component in the ZDMP architecture.
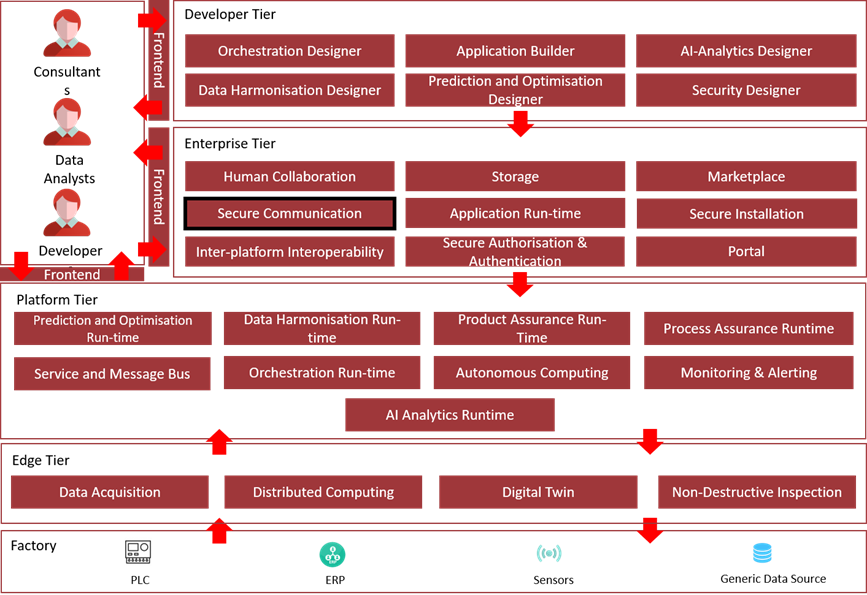
Figure 33: Position of Component in ZDMP Architecture
Benefits
Solve the security aspects that require encryption, data integrity, privacy, and mutual trust
Address the Transport & Application layer security enabling a simplified management of certificates
Features
This component offers the following features:
Retrieve certificates: Recover details (status) of a given certificate
Certificate issuer: Enables T5.2 Authentication & Authorization to request new certificates for new users managed by the Security Command Centre
Certificate download: To download generated certificates in different formats. This enables the user to download the certificate on demand, directly, given correct credentials
Server Certificate issuer: Requests an installed CA to create and store server certificate, with different possible hash methods (initially assume sha256, other possibilities)
Client certificate issuer: To request an installed CA to create and store client certificates, with different possible hash methods (initially assume sha256, other possibilities)
Install Certificate Authorities: To install and manage Certificate Authorities
Inspect details on issued certificates: To request a list of installed certificates and CAs with detailed information
Manage certificates life cycle: To manage revoked certificates, to renew them, or add them to a CRL list
System Requirements
Minimal requirements needed:
Computer with Docker Engine installed (tested in v19.03.8, on Windows)
Security Command Centre
Associated ZDMP Services
Required
How to use
Installation
For ZDMP, it should be installed using the Marketplace and the SecureInstallation, but it could also be deployed standalone OnPremise to miniZDMP using Rancher, or even as standalone resource with docker, if no interaction with other components is needed.
The installation of this component can be done through Docker commands to run docker images. The Secure Communication component can be installed via docker-compose:
Download the latest source code from ZDMP’s GitLab repository Download
Unzip the folder in the desired workspace.
Check the desired configuration parameters in the form of environment variables in the docker-compose file. Two variables can be set, KC-AUTHORIZATION to enable login of the component with KEYCLOAK if the component has been assigned a token, and API_OUTPUT_AS_JSON, to select legacy output or pure JSON responses.
In last versions there is no need to set the KC-AUTHORIZATION to operate with the SCC, it is recommended that the variable is left with its default value, only used for retro compatibility issues.
Also note the Variable DEFAULT_EXPIRE_TIME, which can be adjusted to set the duration of the generated certificates, in seconds.
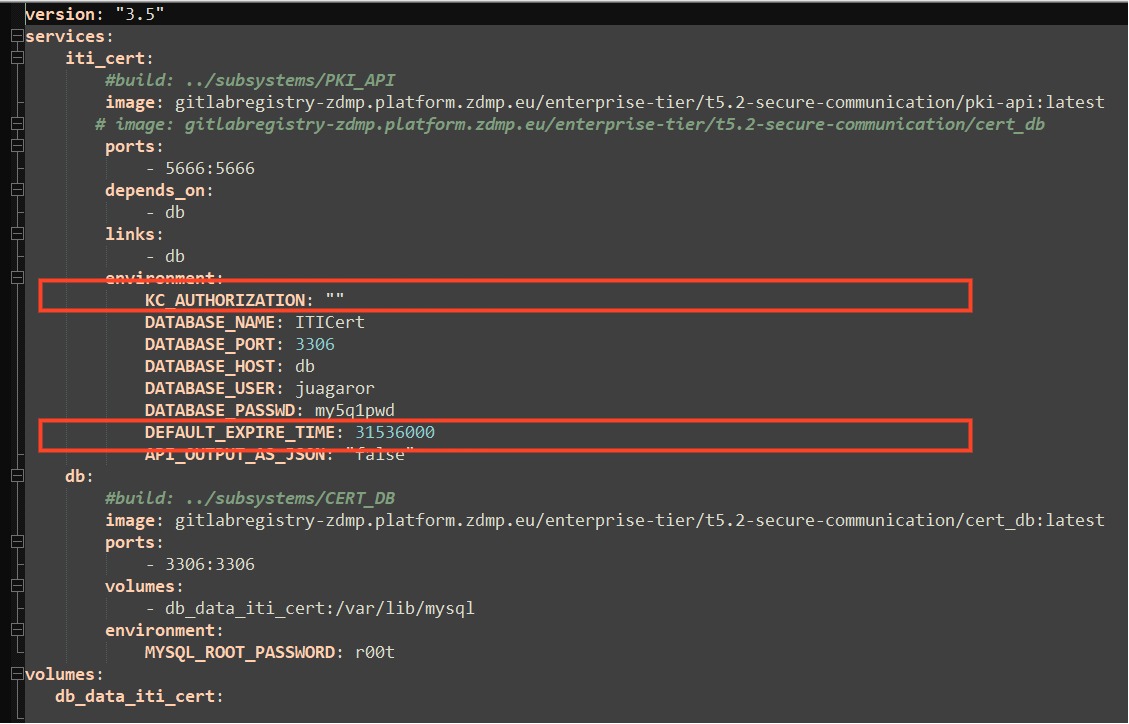
Figure 34: Configuring the secure communications component via docker-compose.
- Through the command line, go to the orchestration folder and run docker-compose command as follows:

- In order to use this component via the Security Command Centre UI, please consider the installation process of Secure Authentication and Authorisation and Secure Installation. Refer to those components for further information:
As for the platform wise installation, the component is deployed to Kubernetes using the helm charts created in conjunction with the Application Runtime, and from the ZDMP Marketplace.
Here is provided a description of the variables that can be set either from SecureInstallation or Rancher.
Select the template version to install and Name as default (it can be changed)
Namespace as default (it can be changed)
Helm Options set to default values
Repository: Image Repository as default or change if using a different repository
Private Registry Settings
Private Registry URL as default if deploying it from standard zdmp repository
Enter the registry user and password and leave the registry secret with
default values
Services and Load Balancing
Service Type to ClusterIP if ingress enabled, otherwise select NodePort.
Ingress Configuration to true or false if enabling ingress to select the ingress domain name to be used.
Storage
- Use Persistence in order to persist data pipelines in a Kubernetes Persistent Volume.
Click on Launch Button
For further details in how to deploy components as part of the Application Run-time, please refer to that component for further instructions:
The corresponding environmental variables can be found in the values.yaml (since version 1.0.5) and are managed in the same pattern as the described above for the local docker-compose process. The only additions are the values nodePort, related to networking in the cluster.
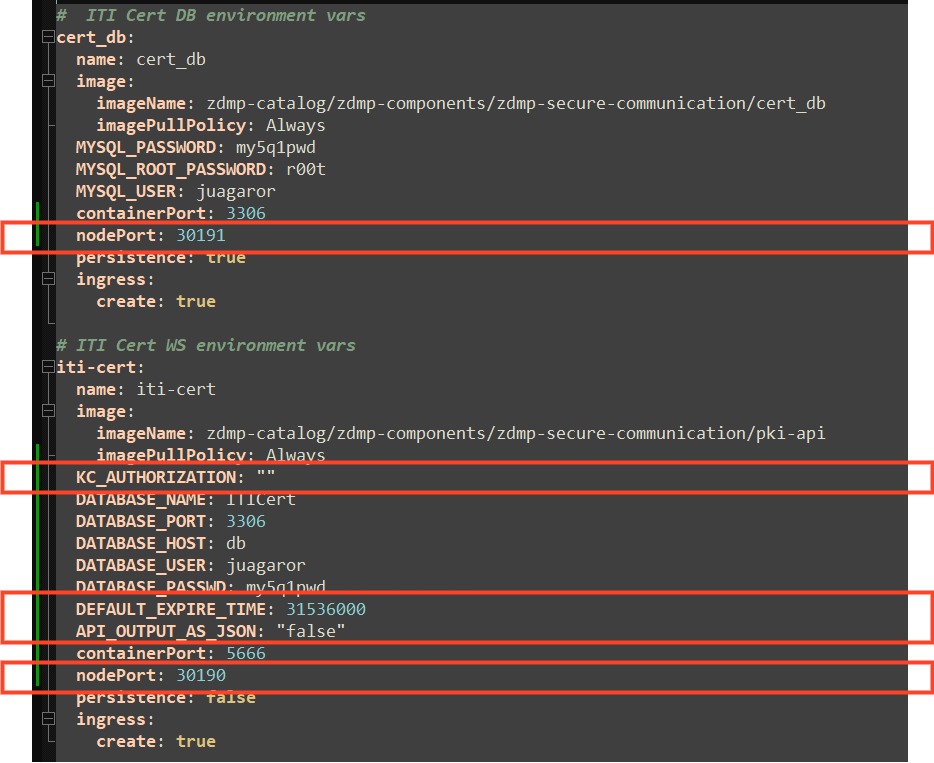
Figure 35 Configuring the secure communications component via helm charts.
Certificate Management
The final usage of this component is envisaged to be through the UI of the Security Command Centre. Nevertheless, a POSTMAN collection is provided, which groups every API call to be tested unitarily, given the user has deployed the Docker Compose file in localhost (if not, it can be performed by editing the calls with the correct URL).
The Security Communication component is also implemented in the Command Centre with the required forms to interact with the Security Communication component. IT administrators are able to install or import a Certificate Authority (CA) through the Security Command Centre UI by providing the CA content and filling in additional parameters such as the encryption algorithm, country, location, and organization name.
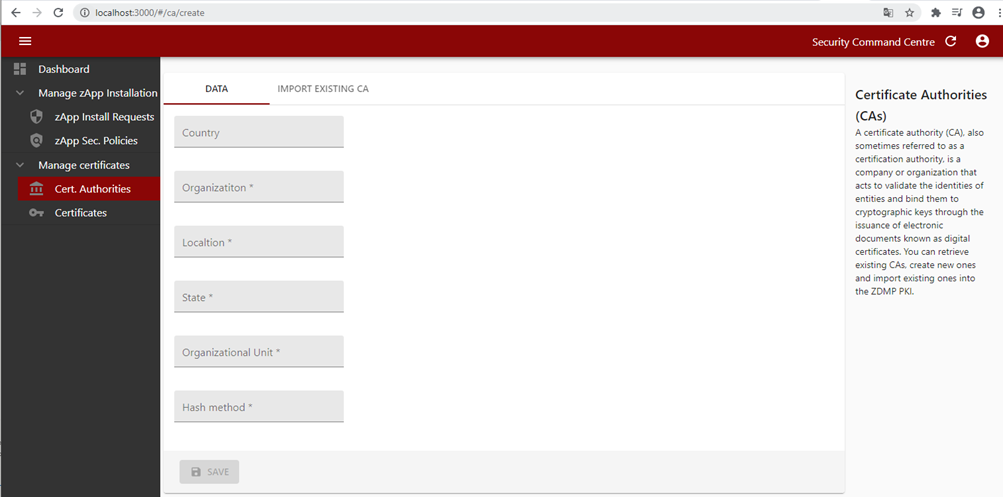
Figure 36: Security command centre CA creation
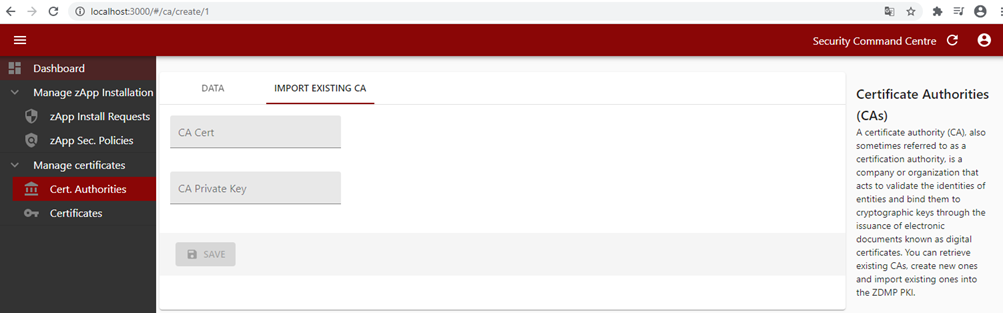
Figure 37: Importing an existing CA
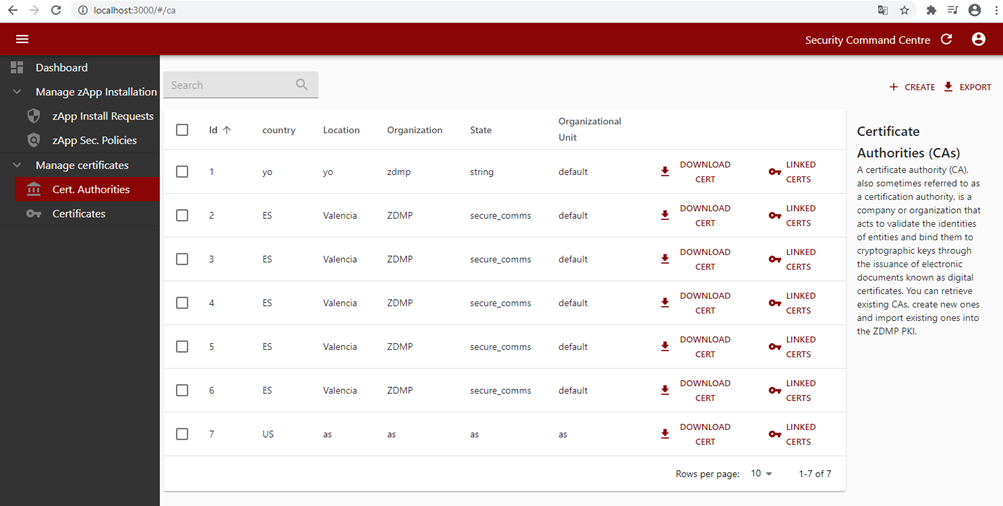
Figure 38: Security command centre certificate authority list
Once the CA is installed, the IT administrator can issue device certificates with the installed CA and download them.
The IT administrator can manage certificates life cycle by revoking already issued certificates, issuing new certificates, or revoking existing ones.

Figure 39: Security command centre certificate list
Finally, to use certificates in any application, follow specific guides according to the protocol of choice. Below an example of using certificates in MQTT or OPC-UA with NODE-RED can be found.
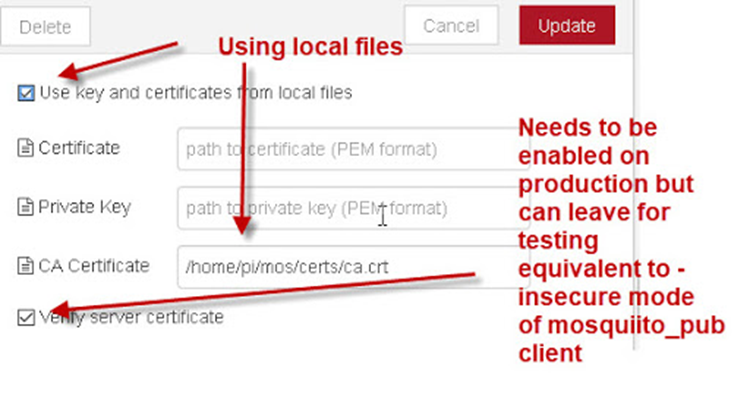
Figure 40 Example of using certificates